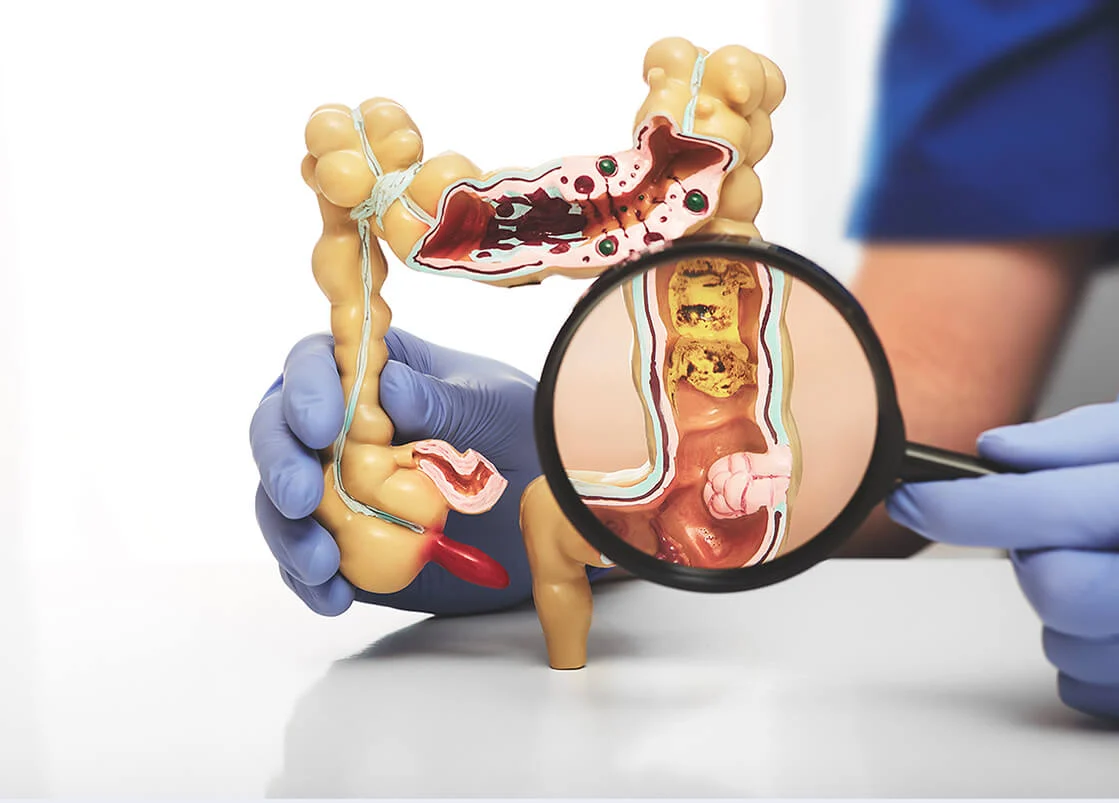
Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a group of bacteria that live in the intestines of both humans and animals. Most strains are part of our normal gut microbiome. However, some can cause serious infections that need quick medical help.
Knowing the causes, symptoms, and tests for E. coli infections is important. This helps prevent complications and ensures proper treatment. This article will give important information about E. coli infections.
What is E. coli?
E. coli is a bacteria found in the intestines of people and animals. Although most strains are harmless, certain varieties can cause severe illness, particularly E. coli O157:H7. This strain is one of the most common causes of foodborne illnesses.
There are more than 200 types of E. coli. The ones that cause serious infections are usually Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC). These strains can cause symptoms like severe stomach cramps, bloody diarrhea, and vomiting. In more serious cases, they can lead to kidney failure, known as Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS).
How Does E. coli Spread?
Contaminated food and water primarily spread E. coli. Additionally, people can transmit it to one another, especially when they do not follow hygiene standards. Common modes of transmission include:
- Contaminated food: Undercooked meat, particularly ground beef, is one of the leading causes of E. coli infections. Other foods, such as unwashed fruits and vegetables and unpasteurized dairy products, can also harbor E. coli bacteria.
- Contaminated water: Drinking or swimming in water contaminated with E. coli can cause infection. This is particularly a concern in areas with poor sanitation or when swimming in lakes or rivers.
To lower the risk of infection, it is important to follow good food safety and hygiene practices. This includes washing hands and cooking meat well.
Examples of E. coli Infection Symptoms
The gastrointestinal symptoms of an E. coli infection can range from mild to severe. Common symptoms include:
- Mild symptoms: Diarrhea (often bloody), stomach cramps, nausea, and vomiting are the hallmark symptoms. Most cases improve within a few days.
- Severe symptoms: In some cases, the infection can lead to serious symptoms. These include high fever, dehydration, and fatigue. Severe abdominal pain and blood in the stool are also significant warning signs.
If symptoms last more than 3 days or get worse, seek medical help right away. This is especially important if you see blood in your stool or have signs of dehydration, like a dry mouth, dizziness, or less urine. Severe infections may lead to complications like kidney failure, which requires urgent medical attention.
Who is Most at Risk?
Certain groups of people are more vulnerable to severe complications from an E. coli infection. These include:

- Young Children: Their immune systems are still developing, making them more susceptible to infections and severe complications.
- Elderly: Older adults, especially those with weakened immune systems or pre-existing health conditions, are at higher risk.
- Immunocompromised individuals include people getting cancer treatments, organ transplant recipients, and those with autoimmune diseases. They have weaker immune systems and may be more likely to get severe E. coli infections.
If you are in a high-risk group and have symptoms of an E. coli infection, get medical help right away.
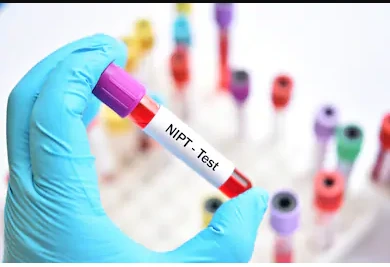
When to Get Tested for E. coli
If you're experiencing symptoms of an E. coli infection, it’s essential to know when to get tested. You should seek testing if:
- Persistent symptoms: Diarrhea, vomiting, or stomach cramps that last more than 3 days should be evaluated by a doctor.
- Blood in the stool: Finding blood in your stool is an important sign of E. coli infection. Get yourself tested right away.
- Severe symptoms: If you cannot keep fluids down, show signs of dehydration or or have a fever, see a doctor right away.
At Parkway Laboratories, we offer E. coli testing to ensure a quick and accurate diagnosis. We help your doctor choose the best treatment for your health.
How E. coli is Diagnosed
Diagnosing an E. coli gastrointestinal infection involves various laboratory tests some common diagnostic tests includes:
- Stool culture test: This is a traditional method of growing stool pathogens on agar culture. It takes at least 48-72 hours for the laboratory to complete the culture process. Culture method can only a limited number of stool pathogens, Specifically, it only detects E. coli O157, one of the many types of shiga toxin producing E. coli.
- Stool PCR test:
- PCR asssays detect tiny amounts of DNA of pathogens present in the stools.
- Researchers can detect many more stool pathogens than traditional stool culture allows.
- This includes all types of shiga toxin E. coli and researchers consider it the offical method in this aspect. In addition, you can obtain results in less than 24 hours.
At Parkway Laboratories, we use advanced testing technologies, including the GIPQS Gastrointestinal Panel PCR - QIAstat-Dx by Qiagen, to provide fast, reliable results. This test can find many germs, like E. coli. It does this accurately and helps your doctor create a good treatment plan.
E. coli Treatment and Prevention
Treatment for E. coli infections typically focuses on symptom management. Most cases can be treated with supportive care:
- Hydration: Staying hydrated is crucial, as diarrhea and vomiting can lead to dehydration. Oral rehydration solutions (ORS) may be recommended to replace lost fluids and electrolytes.
- Antibiotics: While antibiotics are not always needed against most diarrhoea illnesses, they may be used in cases of severe infections or complications. However, antibiotics are generally avoided for certain strains like shiga-toxin E. coli O157:H7, as they can increase the risk of kidney failure.
- Food safety tips: To prevent future infections, always practice good food safety:
- Wash hands thoroughly before eating and after using the bathroom.
- Cook meat, especially ground beef, to a safe temperature (at least 70°C).
- Avoid unpasteurized dairy products and juices.
Prevention is key to reducing the spread of E. coli. Being cautious about food sources, proper hygiene, and avoiding contact with contaminated water are effective measures.
How Our Laboratory Can Help
Parkway Laboratories offers comprehensive e.coli testing Singapore for E. coli infections, ensuring fast and accurate results. Using the latest diagnostic technology, such as GIPQS Gastrointestinal Panel PCR - QIAstat-Dx, we can quickly identify E. coli infections and help your doctor implement the best course of action for treatment.
We know how important it is to get a diagnosis quickly. Parkway Laboratories are made to give fast results. This helps you and your healthcare provider take quick and effective action.
Reach out to your doctor and request to get E. coli tested with us today to ensure a timely diagnosis and treatment plan. Early detection is crucial to prevent severe complications and ensure a faster recovery